Artificial Intelligence: The Way of the Future
A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding AI and Its Impact on Our World
Preface
Technology is moving faster than ever, and few developments shape our world as much as Artificial Intelligence (AI). This ebook is written for people who have heard the term but don’t quite know what it means. You don’t need a technical background. In plain language, we’ll look at what AI is, where it came from, what it does today, and how it will influence our jobs, our laws, our money, and our planet.
[Image for this chapter](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/60/Artificial_intelligence_logo.svg/320px-Artificial_intelligence_logo.svg.png)

Chapter 1: What Is Artificial Intelligence?
AI is when a computer system performs tasks that normally need human intelligence—like learning from data, solving problems, understanding language, or recognizing images.
Everyday examples:
– Voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant
– Autocorrect and translation apps
– Netflix or YouTube recommendations
– Fraud detection by banks
– Smart cameras in phones
While the idea has been around for decades, only recently have we had enough data and computing power to make AI genuinely useful in everyday life.
[Image for this chapter](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/17/Robot_icon.svg/320px-Robot_icon.svg.png)

Chapter 2: A Short History of AI
1950s – First ideas: Alan Turing asks, “Can machines think?” and invents the Turing Test. Early chess and problem-solving programs appear.
1960s–1980s – The expert systems era: Programs that mimic human experts are created for medicine, chemistry, and engineering. Hopes are high, but computers are slow and data is limited. Funding dries up (“AI winters”).
1990s–2000s – Quiet progress: IBM’s Deep Blue beats world chess champion Garry Kasparov. Speech recognition improves. Internet search engines become smarter.
2010s–present – The deep learning boom: Massive data sets and powerful graphics processors allow “deep learning.” Image recognition, translation, and chatbots leap forward. AI starts to show up in phones, cars, and hospitals.
[Image for this chapter](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/5f/Alan_Turing_Aged_16.jpg/320px-Alan_Turing_Aged_16.jpg)

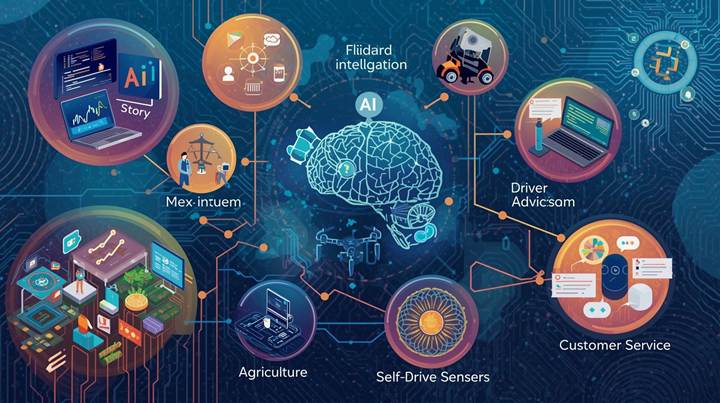
Chapter 3: AI Today
Where you see it now:
– Healthcare: AI helps detect cancer in scans.
– Finance: Fraud detection, credit scoring, and robo-advisors.
– Transportation: Route optimization, driver-assist features, self-driving prototypes.
– Agriculture: Drones and sensors monitor crop health.
– Customer service: Chatbots answer basic questions 24/7.
Why now?
Three forces converged:
1. Huge amounts of digital data.
2. Cheaper, faster computing.
3. New algorithms that can “learn” patterns automatically.
[Image for this chapter](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/5c/Artificial_Intelligence_in_Healthcare.jpg/320px-Artificial_Intelligence_in_Healthcare.jpg)

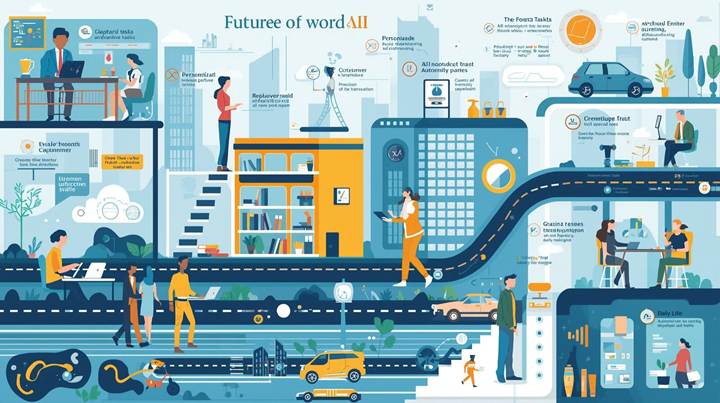
Chapter 4: How AI Will Shape the Future
Jobs:
– Tasks most at risk: Repetitive data entry, routine customer support, basic analysis.
– Jobs that will grow: AI system trainers, ethics specialists, designers of human–AI workflows, creative problem solvers.
– How to prepare: Focus on creativity, empathy, communication, and critical thinking—skills harder to automate.
Daily Life:
– Personalized healthcare, predicting diseases before symptoms.
– Safer and more efficient transportation.
– Education tailored to each student’s pace and style.
– Smarter homes that save energy and time.
[Image for this chapter](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e5/Future_work.jpg/320px-Future_work.jpg)
Chapter 5: Legal and Financial Aspects
Regulation: Governments worldwide are drafting AI laws to address privacy, bias, and safety. The European Union, for example, has proposed strict rules on “high-risk” AI systems.
Liability: If an AI system causes harm—say, a self-driving car crashes—who is responsible: the owner, the developer, or the operator? Legal systems are still figuring this out.
Investment and markets: AI companies attract billions in venture capital. New markets arise for AI tools in healthcare, finance, logistics, and education. Entirely new industries may form around AI ethics, auditing, and safety.
[Image for this chapter](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d7/Scales_icon.svg/320px-Scales_icon.svg.png)


Chapter 6: Environmental & Resource Impact
The cost side: Training large AI models can consume massive amounts of electricity and water (used to cool data centers). This has raised concerns about carbon footprints.
The positive side: AI can optimize supply chains, design more efficient energy grids, reduce waste in manufacturing, and improve crop yields—all of which help the environment.
The future focus: Researchers are working on “green AI”: energy-efficient algorithms and hardware that do more with less.
[Image for this chapter](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8c/Climate_icon.svg/320px-Climate_icon.svg.png)
Chapter 7: Preparing Yourself for the AI Era
Stay informed: Follow reputable news sources, attend webinars or community workshops.
Upskill: Even basic data literacy or coding knowledge can help, but soft skills remain critical.
Ethics and privacy: Understand how your data is used and your rights under new AI laws.
Adaptability: Treat AI as a tool to extend your abilities, not a rival to fear.
[Image for this chapter](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/a3/Online_learning_icon.svg/320px-Online_learning_icon.svg.png)

Chapter 8: Conclusion – The Balanced View
AI is not magic and not doom. It is a tool—powerful, fast, and evolving. Used responsibly, it can make life healthier, safer, and more productive. But it also raises challenges for jobs, privacy, and the planet. The key is understanding, thoughtful regulation, and ethical use. With awareness and preparation, everyone can benefit from the AI future.
Quick Takeaways:
– AI is already woven into daily life.
– It’s the product of decades of research, not an overnight miracle.
– It will change the job market but also create new roles.
– Laws and financial systems are adjusting to its risks and opportunities.
– AI can either strain or help the environment depending on how it’s designed and used.
– Understanding and adaptability are your best tools.
[Image for this chapter](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3f/Balance_icon.svg/320px-Balance_icon.svg.png)